 Purdue University - Extension - Forestry and Natural Resources
Purdue University - Extension - Forestry and Natural Resources
Got Nature? Blog
The classic and trusted book “Fifty Common Trees of Indiana” by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as “An Introduction to Trees of Indiana.”
The full publication is available for download for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
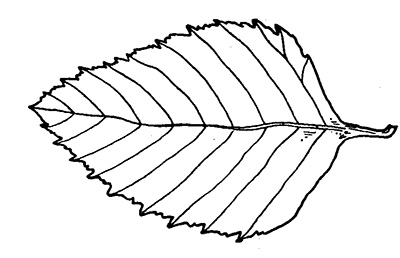
book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the
This week, we introduce River Birch or Betula nigra, which is also known as red birch.
As its name implies, it is found frequently in wet situations. It is often found need waterways and in moist soil areas across the state.
Full article also can be viewed with Purdue Forestry and Natural Resources News: Intro to Trees of Indiana: River Birch
Other Resources:
Birch – Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series
Fifty Common Trees of Indiana
An Introduction to Trees of Indiana
Native Trees of the Midwest-The Education Store, Purdue Extension’s resource center
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest– The Education Store
ID That Tree– YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment-YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands– The Education Store
Forest Improvement Handbook– The Education Store
Wendy Mayer, FNR Communications Coordinator
Purdue University Department of Forestry and Natural Resources
Lenny Farlee, Sustaining Hardwood Extension Specialist
Purdue University Department of Forestry and Natural Resources

Recent Posts
- Announcing-New Indiana Woodland Steward Newsletter
Posted: December 19, 2024 in Forestry, Timber Marketing, Wildlife, Woodlands - Red in Winter – What Are Those Red Fruits I See?
Posted: December 18, 2024 in Forestry, Plants, Urban Forestry, Wildlife, Woodlands - ID That Tree: Prickly Ash
Posted: December 16, 2024 in Forestry, Forests and Street Trees, Urban Forestry, Wildlife - Tips on How You Can Recycle Your Christmas Tree
Posted: in Ask the Expert, Christmas Trees, Forestry, Forests and Street Trees, How To, Wildlife - Hardwood Tree Improvement Regeneration Center (HTIRC) Shares Fall Newsletter, Research and Outreach
Posted: December 13, 2024 in Forestry, Land Use, Natural Resource Planning, Woodlands - Ask An Expert: Holidays in the Wild
Posted: December 9, 2024 in Christmas Trees, Forestry, Forests and Street Trees, How To, Plants, Wildlife, Woodlands - Venison Workshops Help Hunters to Safely Process Deer – ANR
Posted: December 4, 2024 in Forestry, Wildlife, Woodlands - Selecting a Real Christmas Tree
Posted: November 26, 2024 in Christmas Trees, Forestry, How To - Woodland Management Moment: Maintaining Some Open Cover
Posted: November 13, 2024 in Forestry, Urban Forestry, Wildlife, Woodland Management Moment - Help Feed Hungry Hoosiers- MyDNR
Posted: in Community Development, Forestry, How To, Wildlife
Archives
Categories
- Alert
- Aquaculture/Fish
- Aquatic/Aquaculture Resources
- Ask the Expert
- Christmas Trees
- Community Development
- Disease
- Drought
- Forestry
- Forests and Street Trees
- Gardening
- Got Nature for Kids
- Great Lakes
- How To
- Invasive Animal Species
- Invasive Insects
- Invasive Plant Species
- Land Use
- Natural Resource Planning
- Nature of Teaching
- Plants
- Podcasts
- Ponds
- Publication
- Safety
- Spiders
- Timber Marketing
- Uncategorized
- Urban Forestry
- Webinar
- Wildlife
- Wood Products/Manufacturing
- Woodland Management Moment
- Woodlands