About the Composites Manufacturing Simulation Center
Founded in 2015, the Composites Manufacturing Simulation Center (CMSC) of Purdue University has served as the Design Modeling and Simulation Technology Area of the Institute for Advanced Composites Manufacturing Innovation, one of the national manufacturing institutes sponsored by the Department of Energy.

The Composites Manufacturing Simulation Center is located at the Indiana Manufacturing Institute
Purdue University photo
Since its inception, the CMSC has received over $52 million in support from four primary sponsors: the Department of Energy, the National Science Foundation, the Indiana Economic Development Corporation and industry (i.e., Dassault Systémes, one of the Fortune 50 list of the largest software companies that develops software for 3D product design, simulation, manufacturing and performance). Several notable accomplishments of the CMSC to date include fifteen PhD degrees in three of the Schools of Engineering, fifteen industrial internships in sponsor companies, development of the Composites Virtual Factory HUB, a cloud-based manufacturing simulation HUB, and creation of manufacturing workflows appropriate to model-based systems engineering and the Dassault Systémes 3DEXPERIENCE platform:
- ADDITIVE3D — Extrusion Deposition Composites Additive Manufacturing
- PPM3D — Prepreg Platelet Molding and Performance
- INFUSION3D — Resin Transfer Molding
- HYBRID3D — Hybrid Over-molding
- VIRTUAL3D — Digital Twins for ASTM Test Standards

CMSC Composites Virtual Factory HUB
Purdue University photo
The Composites Manufacturing and Simulation Center (CMSC) will celebrate several new accomplishments in 2021. The first is CMSC’s designation in 2020 as the 3DEXPERIENCE Education Center of Excellence of Dassault Systémes. COVID-19 required a virtual celebration of that event and it is appropriate to have an in-person celebration in 2021, to be held Oct. 28th at the Indiana Manufacturing Institute in the Purdue Research Park.
The Dassault Systémes 3DEXPERIENCE Education Center of Excellence in Advanced Composites was established October 28, 2020, is founded on an eight-year partnership between Purdue University and Dassault Systémes (2013-2021) and it is expected that this new level of engagement will bring significant benefits to the two partners and to the global society as their work together bring the advantages of the digital age to society. Together we will advance the digital enterprise by developing the human talent essential to this new paradigm and by utilizing the 3DEXPERIENCE platform to exercise digital twins of complex composites manufacturing and performance to demonstrate the power to predict phenomena that are understood today only by empirical experiences.

Thermwood LSAM 105 in Residence at CMSC
Purdue University photo
They will work together to introduce these concepts to a wide range of industries within the advanced composites community from the original equipment manufacturer level to the supply chain industries. The philosophy of the 3DEXPERIENCE Education Center of Excellence will be to create a learning environment at multiple levels — from advanced research in manufacturing and performance of advanced composites to the engagement of students at all levels needed to build the workforce of the future for Industry 4.0. It is also notable that the West Lafayette Offices of Dassault Systémes were relocated to the Indiana Manufacturing Institute adjacent to CMSC in 2020. The proximity of the two organizations is expected to provide mutual benefits to employees of Dassault Systémes, the faculty and students of Purdue and to their stakeholders.
The second accomplishment is the establishment of the Thermwood Large Scale Additive Manufacturing Laboratory in 2021. Thermwood Corporation is the developer of composites additive manufacturing systems with the scale needed to produce products like the Al Davis Memorial Torch in the Allegiant Stadium in Las Vegas that stands over nine stories tall and is the world’s tallest 3D-printed structure. It is made up of 3D-printed segments made of carbon fiber, reinforced polycarbonate composite and printed on the Thermwood LSAM. Thermwood is located in Dale, Indiana. The Thermwood Large Scale Additive Manufacturing Laboratory will house a Thermwood LSAM 105 with print capacity of volume up to 250 ft. and printing rates of 100 pounds/hour. It will also house the Composites Additive Manufacturing Instrument (CAMRI) that was developed by the CMSC team for validation of virtual twin simulations I additive manufacturing.
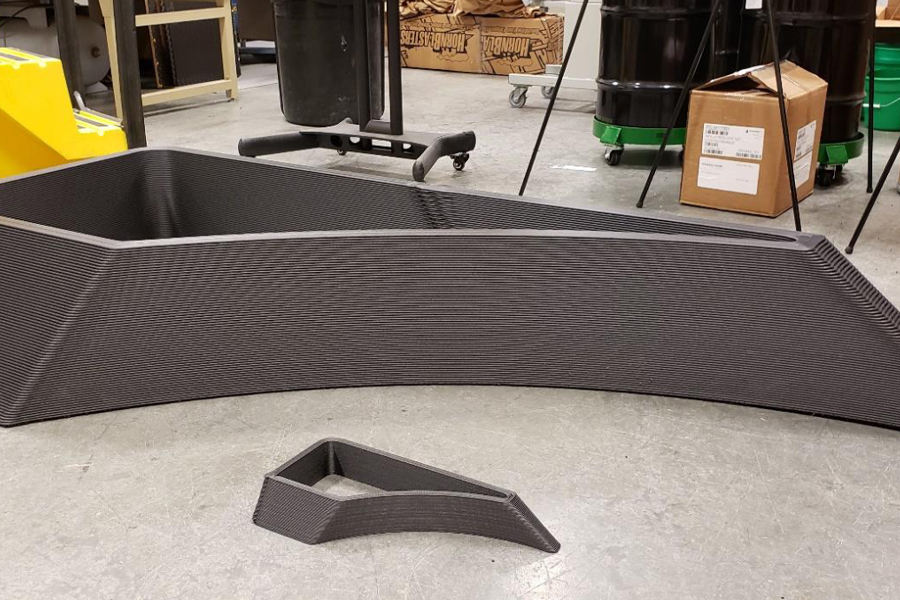

Composites Additive Manufactured Geometry at Two Scales by the Thermwood LSAM 105 and the Purdue CAMRI
Purdue University photo
The third accomplishment to celebrate is the Composites Additive Manufacturing Industrial Consortium, established in 2021, with the goal serving the end user, material supplier and additive manufacturing equipment manufacturing industries in developing this emerging industry. At the foundation of the Consortium is the digital twin of the manufacturing process, ADDITIVE3D, that provides the engineering community with simulations of composites additive manufacturing that can guide successful printing of these large and complex structures and predict performance. Research developed within the consortium will serve to advance composites additive manufacturing for the benefit of consortium members.
The fourth is the accomplishment is the attraction of an outstanding young faculty member to the CMSC and the School of Aeronautics and Astronautics through the Preeminent Teams Faculty Search Program of the College of Engineering, Professor Dianyun Zhang. Dr. Zhang holds the PhD in Aerospace Engineering from the University of Michigan and joins Purdue after her initial faculty appointment at the University of Connecticut Department of Mechanical Engineering. Dr. Zhang was recipient of the National Science Foundation Career Award in 2018 and is the author of several seminal, archival publications in the field of composites manufacturing science and engineering. Her specialties are infusion forming and advanced tape placement composites manufacturing based on a strong applied mechanics foundation.
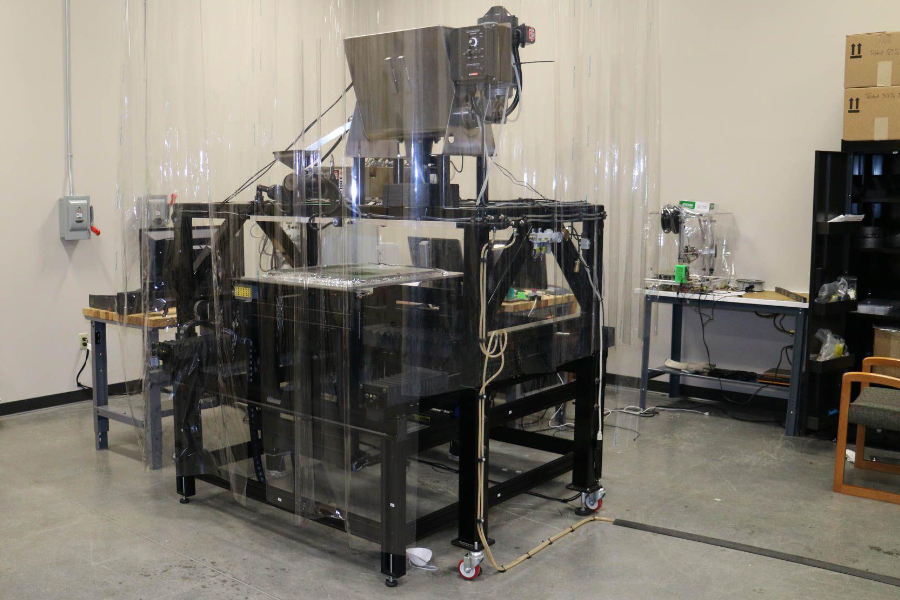

Composites Additive Manufacturing Instrument (CAMRI) Developed at CMSC
Purdue University photo
Another notable accomplishment of the CMSC is the growing relationship of the Boeing Company and Dassault Systémes, in partnership with CMSC, in developing high-rate manufacturing of thermoplastic composites that will find application in current and future aircraft. The model-based engineering and virtual twin technologies of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform serve as the foundation of innovations in aircraft design and manufacturing in the future. The power of the computer software to connect all of the stakeholders in the execution of design, manufacturing and product lifetime support will accelerate product innovation and reduce time to market. This triangular partnership brings Boeing, Dassault Systémes and CMSC together on a shared 3DS OUTSCALE Environment, wherein CAMEO provides the model based engineering structure. This pioneering relationship, platform and computer environment is establishing the future of engineering practice at Boeing.
The CMSC team and the Department of Physics has also been engaged in the design and development of composite structures essential to the next discovery in particle physics with CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research under the support of the National Science Foundation. ATLAS is one of the four major experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Switzerland. Interestingly, carbon fiber advanced composites provide the ideal material for both transparency to high energy particles emitted in the experiments and excellent lightweight structural materials to support the particle detection sensors without distortions. Operating at cryogenic temperatures, the high-energy particle experiments also generate significant heat that must be dissipated by the carbon fiber structure. Therefore, a virtual twin of the Large Hadron Collider support structure is essential to the successful consideration of the multi-physics phenomena governing support structure performance. Successful digital twins of multiple support structures have guided the design and validation of support systems for the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), (ATLAS) and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS).

DMS Computer-Aided Manufacturing System
Purdue University photo

Indiana Manufacturing Institute Conference Space
Purdue University photo

MTS Fatigue Test Frame and Grips
Purdue University photo

CMSC ADDITIVE3D Multiphysics Workflow for Composites Additive Manufacturing
Purdue University photo
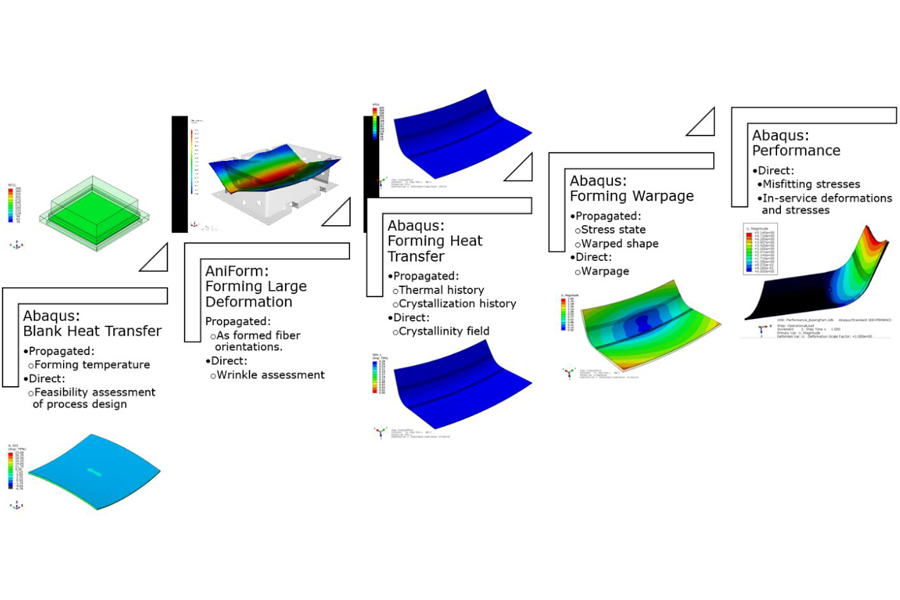
CMSC FORM3D Multiphysics Workflow for Thermoplastic Composites Forming
Purdue University photo